Budget Worksheet
I want make detailed estimates of project activities...
What is it?
The budget worksheet is your tool for identifying, listing, quantifying and costing all of the resources needed to run the activities described in a project plan (eg people, materials and equipment). It is really useful tool to help you create accurate and comprehensive activity based budgets.
The worksheet is a table with a number of pre-set headings and rows for each item in the budget. It is usually set up as a spreadsheet (eg Excel) with formulas to automatically calculate totals. Each project activity area has its own section in the worksheet, with a list of all the resources needed, and in what quantities. This makes it possible to calculate how much each activity will cost to deliver.
How do I use it?
The following scenario from UNITAS explains how the budget worksheet is used in its Capacity Building Project.
The UNITAS team needs to create an activity-based budget for a project to improve the capacity of community partners in the Delta River Region. As part of the budgeting process, Amira creates a budget worksheet. It helps her work out the total cost of the whole project by working out the costs for each of the activities.
The first step in creating the budget worksheet is for Amira to make sure she has all the necessary information available before she starts work on the actual budget. Amira and her team need to have the following:
- Project proposal, log frame (if available) and activity plans with timing
- Budgeting guidance and policy, for things like staff salaries and benefits, indirect costs and inflation rates
- Price lists for commonly-used resources
- Budget worksheet template
For example, one of the activities UNITAS will be running is a series of metalwork skills training workshops. Using project documents the team identify the frequency of workshops, the number of trainees and the costs. They also identify other resources required to deliver the workshops, such as use of the project vehicle. The team use this information to fill out the budget worksheet and produce estimates of the cost for this activity. Here is a part of their budget worksheet:
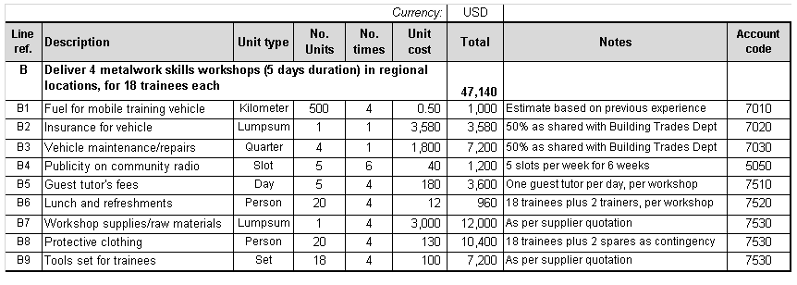
As you review the partially completed budget worksheet, note that:
- The training events are just one of several activities within the capacity building project. The metalwork training activity is given the reference – B. The full budget worksheet will include costs for other activities, which will have different references: A, C and so on.
- Each line in the budget worksheet is given a sequential reference to help the user refer to different lines within the budget.
- Unit type is the basis for calculating the cost of this resource. It helps to think about how the supplier will charge you for this item (by person, by set, by day).
- The number of units describes how many of the items described in the unit type column are needed.
- The next column titled number of times is sometimes called frequency. This captures how many times this resource will need to be used, usually linked to how often this activity will run. In this example there will be four workshops – so in line B9 we need to buy the 18 sets of tools for the trainees, four times.
- Unit cost is the price of one unit of the unit type. It is important that this is accurate and will be the right cost when the project is delivered.
- Total cost is calculated by multiplying the numbers in the three previous columns together (no. units x no. times x unit price).
- Notes – these help to explain where the costs or quantities came from or what assumptions were made. The notes are very useful to help the user understand the budget.
- Account code – each line item is mapped to a relevant account code in the organization’s chart of accounts. This helps the team to summarize the project budget later for internal accounting and reporting systems.
When do I use it?
Budget worksheets are an indispensable tool for project teams when creating project budgets. They are prepared during the planning phase of the project, making use of the information developed during project design. They help to ensure budgets are accurate and complete, provide all the information needed to justify the costs included and are easy to update with changes to project plans or the scope of activities.
Who is involved?
The budget worksheet is prepared and used by the project team as it is a critical stage in developing the project budget. The finance team may review or use the document but the project team should prepare it.
The information in the budget worksheet document is very detailed and more senior managers may prefer more of an overview in a more summarized format, like the income and expenditure budget.
Tips:
When estimating the unit cost, make sure that you use a cost that is as accurate as possible for the time when the activity or project will be implemented. Prices often rise between the time they are estimated and when the expense occurs. Don’t use a random guess or the price you have paid in the past. Get an up to date quote or use a current price and if necessary, include an amount for inflation. If you get this wrong, it will distort your budget and you won’t have enough money to implement your activities.
If your activities are very complex and use lots of resources, it is a good idea to use a table to break each activity down into tasks. For each task you should list the different resources required, the quantities needed for each resource and the timeframe (when) they will be needed. This table is often called a project breakdown sheet.

Supported & Developed by:
Shared by:
Users are free to copy/redistribute and adapt/transform
for non-commercial purposes.
© 2022 All rights reserved.



















 .
.